Best practices for fertilizer trials
Enhancing crop nutrition through informed decision-making
Introduction
Fertilizer trials play a crucial role in determining the optimal nutrient management strategies for crops, helping agronomists, researchers, and farmers maximize crop productivity while minimizing environmental impacts. This article outlines the best practices for designing and conducting fertilizer trials, with a focus on the benefits of using QuickTrials to streamline the trial process and deliver valuable insights.
Trial design and planning
A well-planned trial design is crucial for obtaining reliable and statistically valid results. Here are some important factors to consider:
1. Objectives and hypotheses

Clearly define the trial objectives and hypotheses, guiding the selection of treatments, experimental design, and data collection methods.
2. Treatments

Test various fertilizer types, formulations, application rates, and timings to comprehensively evaluate their effects on crop growth and yield.
3. Experimental design
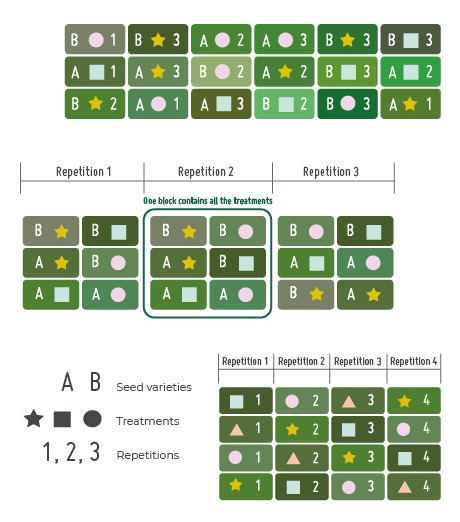
Employ suitable designs, such as randomized complete block, factorial, or split-plot designs, tailored to the trial objectives and constraints. QuickTrials can help you create randomized and replicated trials with ease, allowing for optimal trial design.
4. Replication

Include multiple replications of each treatment to account for random variation and enhance result reliability.
Data collection and management
Accurate data collection and effective data management are critical for successful fertilizer trials. Consider the following guidelines:

1. Consistent data collection methods:
Develop standardized protocols for data collection, and ensure that all team members adhere to them.

2. Plan site visits:
Schedule field staff visits to coincide with key growth stages or intervals. QuickTrials can facilitate the planning, coordination, and monitoring of site visits, ensuring optimal timing and efficiency.

3. Digital data collection tools:
Utilize digital platforms like QuickTrials to collect, store, and manage data efficiently and securely. QuickTrials enables data entry and validation on mobile devices, reducing errors and streamlining the data management process.

4. Relevant data parameters
Collect data on crop growth, yield, and nutrient uptake, as well as soil nutrient status and other relevant environmental factors to better understand the effects of fertilizer treatments.

5. Monitor and validate:
Regularly monitor and validate data collection to identify gaps or outliers. QuickTrials allows trial coordinators to verify collected data centrally in near real-time, enabling immediate feedback and coordination of corrective actions when needed.
Data analysis and interpretation
Accurate data analysis and interpretation are essential for drawing meaningful conclusions from fertilizer trials. Keep these recommendations in mind:
1. Employ suitable statistical methods:
Use appropriate statistical tools to analyze the data, determine the significance of observed differences between treatments, and identify interactions between factors.
2. Assess treatment efficacy under various conditions:
Evaluate fertilizer performance under different environmental conditions and management practices to identify the most effective strategies for specific contexts.
3. Generate practical recommendations:
Translate trial results into actionable insights for farmers, researchers, and other stakeholders to implement in their nutrient management practices.
QuickTrials offers built-in data analysis and visualization tools, as well as support for many third-party tools and integrations, providing a robust foundation for consistent trial analysis across an organization.

Communication and dissemination
Effectively communicating trial results is crucial for promoting their adoption in the field. Follow these guidelines:

1. Adapt your message
Present trial findings in an easily understandable and relevant format for your target audience, using clear language and visuals.

2. Utilize digital platforms:
Leverage websites, social media, and other digital channels, to share trial results and engage with stakeholders.

3. Seek feedback:
Encourage feedback from stakeholders to refine future trial design and execution and improve nutrient management strategies.







